Jogging, a low-intensity form of running, is a popular choice among beginners and individuals seeking a less strenuous workout. While jogging may not be as intense as high-intensity exercise, it offers numerous benefits for cardiovascular fitness and weight management.
Jogging is a popular form of cardiovascular exercise that not only gets your heart pumping but also engages a variety of muscle groups throughout your body. Whether you’re a seasoned runner or just starting out on your jogging journey, understanding the muscles involved can help you optimize your workout routine and achieve your fitness goals more effectively.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of jogging and explore the specific muscles it targets and explain what muscles does jogging work, more providing you with valuable insights to enhance your running experience and overall fitness. Whether you’re looking to tone your legs, strengthen your core, or improve your overall health, jogging can be a key player in achieving those objectives.
Although jogging may not be specifically designed to build muscles, it can contribute to overall muscle tone and endurance.
Incorporating jogging into your training program can be a valuable addition, providing a place for low-intensity activity while still helping you achieve your fitness goals.
With its improved cardiovascular health, reduced risk of injury, and other benefits, jogging offers a suitable choice for individuals looking to stay active and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Table of Contents
What is the Jogging?

Jogging is a form of aerobic exercise that involves running at a slow or moderate pace. It is characterized by a steady and continuous movement, typically at a speed slower than running.
Jogging is commonly performed as a recreational activity, fitness workout, or part of a training routine. It is a popular choice for individuals of all fitness levels, including beginners, as it provides a lower-impact alternative to running.
Jogging offers various positive effects on health, such as enhanced stamina of the heart and lungs, weight management, and overall fitness. It can be enjoyed outdoors or on a treadmill, making it a flexible and accessible exercise option.
Jogging Form
Jogging and running have slightly different forms, with proper jogging form involving less knee lift and less swinging of the arms compared to proper running form. This is because jogging is done at a more moderate speed, which necessitates less force and motion.
However, jogging allows for longer periods of exercise due to the conserved amounts of energy. While jogging primarily focuses on cardiovascular endurance and calorie burning, it can still contribute to enhancement of muscular build, especially in the lower extremities.
The repetitive nature of jogging helps to strengthen and tone muscles over time, resulting in improved muscle definition and overall fitness. So, while jogging may not build muscles to the same extent as high-intensity resistance training, it can still provide a beneficial impact on muscle health and toning.
What Is Jogging Workout?
A jogging workout involves moving at a leisurely pace, with individuals taking spring steps and maintaining a comfortable trot. It is a form of aerobic exercise that utilizes oxygen as fuel, providing a healthy activity to enhance stamina and endurance.
Jogging is characterized by a visual perspective of bouncing movement, where strides, knee elevation, and arm swing contribute to a fluid and natural motion. With its casual approach, jogging allows individuals to push their boundaries at their own pace, promoting a positive mindset towards fitness. It is an excellent outlet for lifetime joggers to engage in a healthy activity, improve energy conservation, and maintain a leisurely pace. Read more about Yoga can grow muscles.
Incorporating jogging into a training schedule contributes to overall well-being and a sense of achievement. By focusing on a leisurely pace and adopting a casual approach, jogging offers a healthy activity that promotes a positive mindset and allows individuals to connect with their bodies and enjoy the benefits of outdoor exercise.Study more about the difference between jogging, running and sprinting.
What Muscles Does Jogging Work?
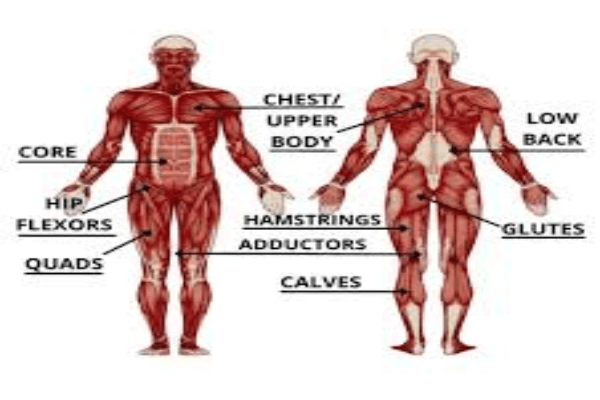
Jogging is a fantastic form of exercise that effectively engages multiple muscle groups in the body. Jogging, often hailed as one of the most accessible and effective forms of exercise, goes beyond just providing cardiovascular benefits. It’s a comprehensive workout that engages a wide array of muscles throughout your body, resulting in not only improved endurance but also enhanced strength and stability.
Lower Body Muscles
One of the primary areas that jogging targets is the lower body. As you stride forward and push off the ground with each step, your quadriceps, located at the front of your thighs, play a crucial role in extending your knee. Simultaneously, the hamstrings at the back of your thighs act to flex the knee while propelling your leg backward.
The calf muscles, including the gastrocnemius and soleus, work to lift your heels off the ground during each stride. Your glutes, the powerful muscles in your buttocks, are engaged as you push off the ground with each step, helping propel your body forward. Moreover, the hip flexors, located at the front of your hips, are responsible for lifting your knees toward your chest as you jog.
Upper Body and Core
Although jogging primarily emphasizes the lower body, it’s not a workout that neglects the upper body and core muscles. Your arms are not just along for the ride; they swing rhythmically with your strides, providing a counterbalance and aiding in maintaining momentum. This arm movement engages the muscles of the arms, shoulders, and upper back.
Furthermore, your core muscles play a crucial role in stabilizing your body and maintaining an upright posture while jogging. These muscles include the rectus abdominis (the “six-pack” muscles), the obliques, and the transverse abdominis, all of which work together to support your spine and pelvis.
Other Muscles
Incorporating jogging into your fitness routine offers a multitude of advantages. Not only does it boost cardiovascular health and stamina, but it also helps you tone and strengthen various muscle groups throughout your body. This holistic approach to exercise ensures that you’re not only burning calories and shedding excess weight but also building a strong and well-balanced physique.
So, when you hit the jogging trail or hop on a treadmill, you’re actively working on enhancing your overall muscular endurance, strength, and stability, making it a well-rounded workout for your entire body. Whether you’re striving for toned legs, a strong core, or improved overall fitness, jogging has got you covered.
Does Jogging Burn Fat?
Jogging, a form of running, is widely recognized as an effective fat-burning exercise. According to the American Council on Exercise, jogging helps individuals in losing weight by burning a significant number of calories. Data shows that a runner, regardless of their weight, can burn a substantial amount of calories in just 10 minutes of steady-paced jogging.
This makes jogging a favorable option for those seeking to shed excess pounds and achieve their weight loss goals. In terms of fat burning, jogging has been proven to beat other forms of exercise in its ability to promote weight loss. Incorporating regular jogging sessions into your fitness routine can yield positive results in your fat burning journey.
Jogging When Pregnant ?
Jogging during pregnancy can contribute to building muscles while keeping you and your baby healthy and happy.
It is generally recommended to continue jogging if you were doing it before pregnancy, as long as your doctor approves. Jogging can also help reduce stress and maintain a healthy activity level during pregnancy.
What Is the Difference Between Running And Jogging?
When it comes to differentiating between running and jogging, one crucial factor to consider is speed. While jogging is often seen as a slower version of running, experts define jogging as maintaining an average pace ranging from 4 to 6 miles per hour.
On the other hand, running is characterized by a faster pace that exceeds 6 mph or a pace quicker than a 10-minute mile. This distinction in speed sets running apart as a more intense and faster form of aerobic exercise compared to jogging.
However, both activities offer their own unique benefits and can be tailored to individual fitness goals and preferences.
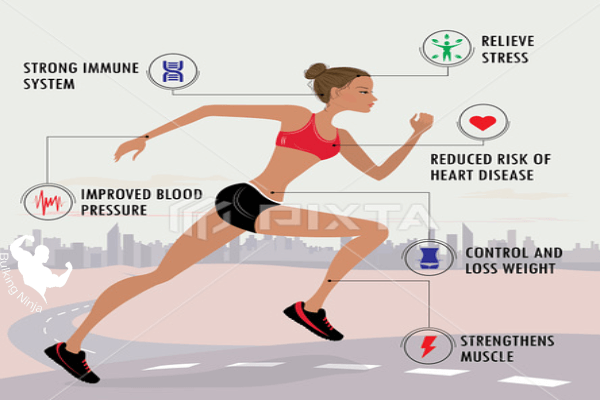
Best Benefits of Jogging?
Jogging offers a wide range of benefits that positively impact both physical and mental health.
Improve Cardiovascular , Regular jogging can help improve cardiovascular fitness, enhancing the overall functioning of the heart and circulatory system.Jogging aids in weight management by burning calories and promoting a healthy body weight.
It releases endorphins, It prompts the release of endorphins, which are natural mood-enhancers boosters, leading to reduced stress levels and improved mental well-being.
Jogging is an effective way to relieve stress and clear the mind, providing a sense of relaxation and rejuvenation.
Enhanced Overall Fitness.
Jogging engages various muscle groups, including the lower body (quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, glutes) and the core, leading to improved strength and endurance.
Maintain Healthy Bone Density ,It helps maintain healthy bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Jogging Increases Lung Capacity and improves respiratory function, leading to better endurance during physical activities.
Improved Flexibility , Regular jogging sessions contribute to improved flexibility and joint mobility.
Disease Prevention and Longevity
Jogging plays a significant role in preventing chronic diseases such as hypertension, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes.
It helps regulate blood pressure, reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, and improve insulin sensitivity.
Regular jogging has been associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases, certain cancers, and metabolic disorders.
Studies suggest that joggers tend to live longer and have a lower mortality rate compared to non-joggers.
Accessible and Cost-Effective
Jogging is accessible to almost everyone, as it requires minimal equipment and can be done in various settings.
It is a cost-effective exercise option, eliminating the need for gym memberships or expensive equipment.
Jogging can be easily incorporated into daily routines, allowing individuals to reap its benefits without major time commitments.
Always make sure to seek advice from a medical expert before starting any new exercise program, including jogging, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does jogging make your leg muscles bigger?
No, jogging alone may not make your leg muscles significantly bigger. High-intensity, short-duration running like sprinting is more likely to build leg muscles. Long-distance running may not have the same muscle-building effect and can even inhibit muscle growth due to significant muscle damage.
Is jogging enough exercise for legs?
Jogging alone may not be enough exercise to fully target and strengthen your leg muscles. It is beneficial to incorporate other activities like weight lifting, swimming, yoga, or Pilates to complement your jogging routine. These exercises can help target specific muscles, improve running form, enhance gait efficiency, and strengthen your bones.
What does jogging do to your legs?
Jogging engages and works all the muscles in your legs, both large and small. With consistent jogging, you can expect to develop lean muscle in your legs and improve your endurance over time.
Should I train legs if I run a lot?
Yes, it is recommended to train your legs even if you run a lot. Incorporating strength training sessions 2-3 times a week can help strengthen your leg muscles and improve overall running performance. It’s important to allow your muscles at least one day to recover from the strain by giving them proper rest.
Does jogging make your calves bigger or smaller?
Jogging can make your calves bigger if you have slim calves and develop muscle through running. However, if you have extra fat, jogging may lead to a reduction in calf size. The effect of jogging on calf size can vary depending on individual factors such as muscle development and body composition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the benefits of jogging extend far beyond its role as a cardiovascular workout. This dynamic exercise engages a symphony of muscles throughout your body, from the lower body powerhouses like the quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, glutes, and hip flexors, to the upper body and core muscles that provide balance and stability.
By understanding the diverse muscle groups involved, you can maximize the advantages of jogging, whether you’re aiming to sculpt your physique, build endurance, or simply improve your overall health.
So, the next time you lace up your running shoes and head out for a jog, remember that you’re not just working on your heart and lungs; you’re giving your entire body a well-rounded and invigorating workout that contributes to a healthier, fitter you. Embrace the joy of jogging, and let it propel you toward your fitness goals while keeping your muscles strong and your body in peak condition.
Jogging can indeed build muscles, particularly in the legs. It targets and strengthens various muscles in the lower body, leading to increased muscle development and endurance.
However, the extent of muscle growth may vary depending on factors such as the level of exertion, length of time, and personal attributes. Incorporating strength training exercises alongside jogging can further enhance muscle development and overall fitness.














