“When it comes to sculpting powerful and well-defined legs, there’s a multitude of exercises to choose from, but one that stands out as a tried-and-true favorite is the dumbbell lunge.
Whether you’re a seasoned fitness enthusiast or just starting on your journey to stronger legs, you’ve probably encountered this versatile exercise at the gym. But what makes dumbbell lunges so special, and are dumbbell lunges good for legs muscles, they truly effective for building leg muscles?
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the world of dumbbell lunges, exploring their benefits, proper form, and the science behind their impact on your leg muscles. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of whether dumbbell lunges should be a staple in your leg day routine.”
Table of Contents
Are Dumbbell Lunges Good for Legs Muscles?
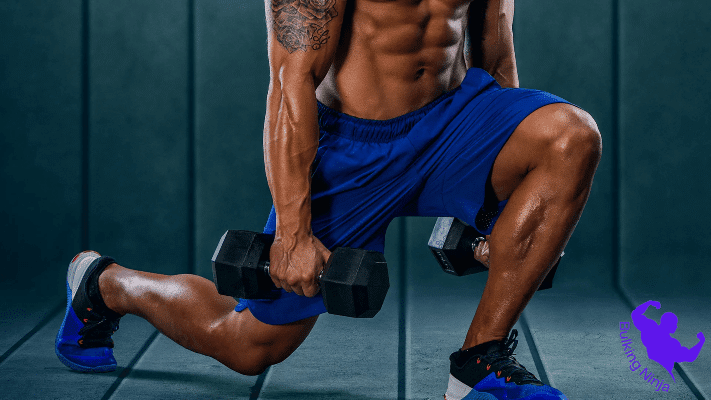

Dumbbell lunges are a quintessential strength training exercise that can significantly strengthen and sculpt the leg muscles, enhancing overall lower body tone. By integrating these lunges into your fitness routine, you can effectively improve the stability and mobility of your hips and back, crucial for optimal athletic performance.
As resistance exercises, dumbbell lunges target specific muscles, making them an ideal choice for athletes, especially runners and cyclists, aiming to enhance their leg strength and endurance. Additionally, exploring the variation options of dumbbell lunges can provide an added advantage, allowing you to customize your workout regimen and experience even more pronounced benefits.
For a comprehensive understanding of how dumbbell lunges can positively contribute to your leg muscles, continue reading to unveil the numerous benefits they offer.
What is Dumbbell Lunges Exercise?
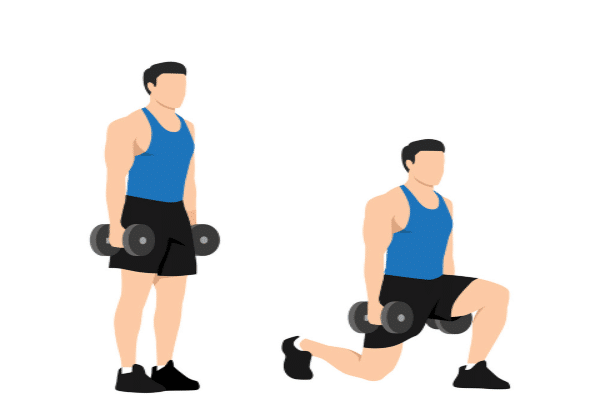
Dumbbell lunges are a popular and effective strength training exercise that primarily targets the muscles in the lower body, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. They are performed by holding a dumbbell in each hand, allowing for an added resistance that intensifies the workout. Read more about Body Weight Exercises.
To execute a dumbbell lunge, one typically steps forward with one leg while bending both knees to create a 90-degree angle, then returns to the starting position. This exercise not only helps build leg strength but also enhances balance, stability, and overall lower body coordination. Dumbbell lunges are often incorporated into various workout routines, whether for muscle building, toning, or general fitness improvement.
How to do Dumbbell Lunges workout?
Performing dumbbell lunges involves the following steps:
Starting Position
Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand by your sides, palms facing your body.
Step Forward
Take a controlled step forward with one leg, ensuring your front knee is at a 90-degree angle and your back knee is almost touching the floor. Maintain an upright posture throughout.
Pause and Return
Pause briefly at the bottom of the lunge, then push back up to the starting position using your front heel to propel yourself. Make sure to engage your core for stability.
Alternate Legs
Repeat the movement with the opposite leg, alternating back and forth to complete a set.
Tips for an effective dumbbell lunge workout:
Maintain proper posture throughout, keeping your chest up and your shoulders back.
Ensure that your knee does not extend past your toes during the lunge to prevent strain.
Control your movements to focus on engaging the targeted leg muscles.
Start with lighter weights to perfect your form before increasing the load.
Incorporate dumbbell lunges into your workout routine to strengthen and tone your lower body, fostering overall stability and balance.
Does dumbbell lunges Build Legs Muscles?
Dumbbell lunges are a compound exercise that effectively engages multiple muscle groups in the lower body. When you perform a dumbbell lunge, the quadriceps, located in the front of the thighs, are activated to extend the knee as you push back up to the starting position. The hamstrings, situated at the back of the thighs, play a significant role in stabilizing and controlling the descent as you lower your body during the lunge.
Furthermore, the glutes, the large muscles of the buttocks, are intensely engaged throughout the entire movement. These muscles are pivotal for hip extension and play a crucial role in generating power during the upward phase of the lunge.
The added resistance provided by the dumbbells intensifies the workload on these muscle groups, encouraging muscle hypertrophy, which is essential for muscle growth and development. By gradually increasing the weight and resistance, you can continually challenge your muscles, promoting further strength gains and muscular adaptation over time.
Which Muscles Are used In dumbbell lunges?
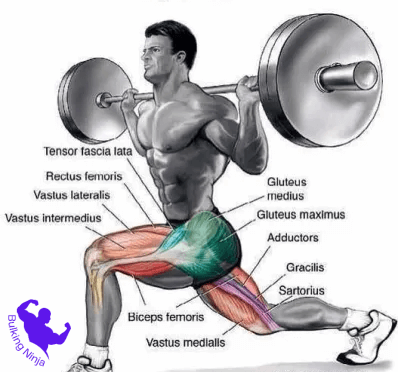
Dumbbell lunges are a highly effective compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, primarily targeting the lower body. The key muscles involved in the execution of dumbbell lunges include:
Quadriceps
The quadriceps, located in the front of the thighs, are actively engaged during the upward phase of the lunge. They play a vital role in extending the knee and are crucial for movements like walking, running, and jumping.
Hamstrings
Situated at the back of the thighs, the hamstrings assist in controlling the descent during the lunge. They help in bending the knee and are essential for various lower body movements and overall lower body strength.
Gluteal Muscles (Glutes)
The glutes, which comprise the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, are the primary movers during the lunge. They aid in hip extension and play a critical role in stabilizing the pelvis and supporting the body’s weight.
Calves
The calf muscles, specifically the gastrocnemius and soleus, are also engaged to a certain extent during the lunge, especially when pushing back up to the starting position.
Core Muscles
Although not the primary focus, the core muscles, including the abdominal muscles and the muscles along the back, are activated to maintain stability and balance throughout the movement.
By targeting these major muscle groups, dumbbell lunges offer a comprehensive lower body workout that not only helps build muscle strength and endurance but also promotes overall lower body stability and balance.
Benefits of performing lunges
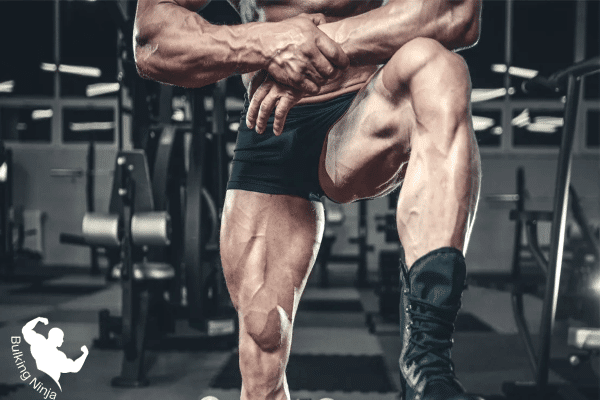

Lunges and Muscle Development
Dumbbell lunges, when executed correctly, work the large muscle groups in the lower body, aiding in the development of lean muscle mass. This contributes to a more defined lower body appearance, helping individuals achieve their desired physique and promote a positive body image.
Weight Management and Metabolism
Incorporating dumbbell lunges into a regular workout routine can be advantageous for those aiming for weight loss. By engaging large muscle groups, lunges can help reduce body fat and increase the resting metabolism, allowing individuals to burn more calories even during periods of inactivity.
Improving Stability and Balance
The unilateral nature of lunges promotes balance and stability, as they activate stabilizing muscles, enhancing coordination and overall body balance. This not only fosters a more stable and agile physical foundation but also aids in the prevention of injuries, providing a secure base for further exercise progression.
Optimizing Posture and Alignment
Dumbbell lunges contribute to improved posture and spinal alignment by strengthening the core and back muscles without exerting excessive strain. This enhanced spinal stability can help individuals stand taller, facilitating better overall body alignment and minimizing the risk of strain-related injuries.
Tailored Training Approaches
Incorporating single-leg movements, heavy weights, and high-intensity circuit training routines can provide added benefits, especially in rehabilitation scenarios. By addressing imbalances and misalignments, individuals can ensure a more symmetrical and well-balanced body, mitigating the risk of overuse injuries and promoting a holistic approach to muscle development and rehabilitation.
Benefits by type of lung
Stationary lunges
The primary focus of stationary lunges is on your glutes, quadriceps, and hamstrings. In this exercise, your front leg bears the majority of your weight, while your back leg is crucial for maintaining balance, stability, and overall body support. Mastering the form of stationary lunges is essential as they form the basis for various lunge variations.
Side lunges
Engaging in lateral lunges promotes the enhancement of balance, stability, and muscular strength. These exercises specifically target the inner and outer thighs and might contribute to reducing the visibility of cellulite. By incorporating side-to-side movements, side lunges introduce a refreshing deviation from the typical forward or rotational motions of the body.
Moreover, they effectively engage the quadriceps, hips, and legs from a slightly different perspective, offering a unique workout experience. While performing these lunges, it is crucial to focus on the activation of the muscles on the outer sides of your legs.
Walking lunges
Executing walking lunges requires both balance and coordination. This particular variation emphasizes the core, hips, and glutes, effectively enhancing overall stability. Moreover, they contribute to an expanded range of motion and aid in refining functional movements utilized in everyday activities. For an added challenge, incorporating weights or introducing a torso twist can intensify the benefits derived from walking lunges.
Reverse lunges
Reverse lunges engage your core, glutes, and hamstrings while exerting minimal pressure on your joints, providing increased stability for the leading leg. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with knee issues, balancing difficulties, or limited hip mobility.
By incorporating reverse lunges, you enhance your balance during backward movements, diversifying the direction of your exercise routine and prompting your muscles to adapt to varied movement patterns.
Lunges and squats
Incorporating lunges and squats into your workout routine is beneficial for strengthening your lower body. Opt for lunges if you experience low back pain, as they tend to exert less pressure on your back. Conversely, if you find greater stability in the squat position, prioritize this exercise instead.
Given that both exercises offer similar benefits, your choice between the two should be based on personal preference and what yields the best results for your body. Nonetheless, including both lunges and squats in your regimen can be advantageous for overall fitness.
Twist lunges
To intensify engagement of your core and glutes, consider incorporating variations into your stationary, walking, or reverse lunges. Introducing twists during lunges not only demands enhanced balance and stability but also encourages the alignment of your knees as you rotate your upper body away from your lower body. Moreover, this exercise will stimulate the muscles in your ankles and feet as well.
Curtsy lunge
Curtsy lunges effectively build and firm your glutes, contributing to better posture and overall stability. Strengthening these muscles can effectively reduce the risk of back and knee discomfort, consequently enhancing athletic performance and minimizing the likelihood of injuries.
Furthermore, curtsy lunges aid in sculpting and fortifying your hip adductors, quadriceps, and hamstrings while simultaneously refining hip stabilization. For a more challenging workout, consider incorporating a kettlebell or dumbbell to intensify this variation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 3 benefits of doing lunges?
Three benefits of doing lunges include:
- Improved lower body strength.
- Enhanced balance and stability.
- Increased flexibility in the hip flexors and hamstrings.
What are 6 benefits of lunges?
Strengthening leg muscles
Improving core stability
Enhancing balance and coordination
Increasing hip flexibility
Boosting functional movement patterns
Engaging multiple muscle groups for efficient workouts.
Are dumbbell lunges better than squats?
No, dumbbell lunges are not necessarily better than squats; they serve different purposes. Lunges offer more balance and coordination challenges, and target each leg independently, while squats are excellent for overall lower body strength and target the glutes and quads more effectively. Both are valuable in a balanced workout routine.
What muscles do dumbbell lunge target?
Dumbbell lunges primarily target the quadriceps (front of the thighs), glutes (buttocks), hamstrings (back of the thighs), and calves. They also engage the core muscles for balance and stability.
Do dumbbell lunges burn belly fat?
Dumbbell lunges can contribute to overall fat loss, including belly fat, as part of a comprehensive fitness routine and a calorie-controlled diet. However, they do not specifically target belly fat, as spot reduction of fat in specific areas is not possible through exercise alone.
What is the main target of lunges?
The main target of lunges is the lower body muscles, primarily the quadriceps (front of the thighs), glutes (buttocks), and to a lesser extent, the hamstrings (back of the thighs) and calves. Lunges also engage the core muscles for stability and balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dumbbell lunges are indeed a highly effective exercise for strengthening and building leg muscles. They offer a dynamic range of motion that targets the quads, glutes, hamstrings, and calves, while also engaging the core and improving balance.
With the versatility to modify intensity and difficulty through weight adjustments or variations in form, lunges cater to all fitness levels. However, it’s crucial to maintain proper form to maximize benefits and prevent injury.
Whether you’re looking to enhance muscle tone, boost strength, or improve functional fitness, incorporating dumbbell lunges into your leg workout routine can yield significant benefits. Remember, consistency and proper technique are key to unlocking the full potential of this powerful exercise for your leg muscles.